Case study: Heartstart Malvern - empowering pupils with lifesaving CPR skills
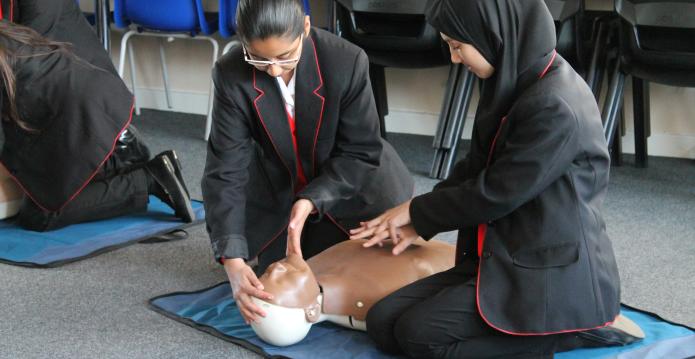
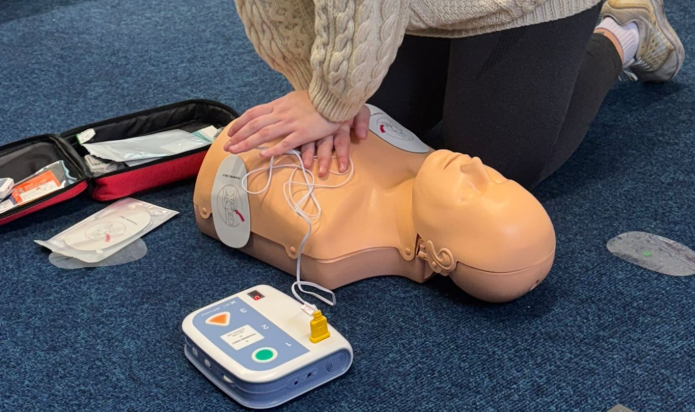
A small charity in Worcestershire is making a big difference when it comes to equipping young people with lifesaving skills. Since launching in 2017, Heartstart Malvern has provided free CPR training to nearly 6,500 people, including hundreds of school children across the local area.
-